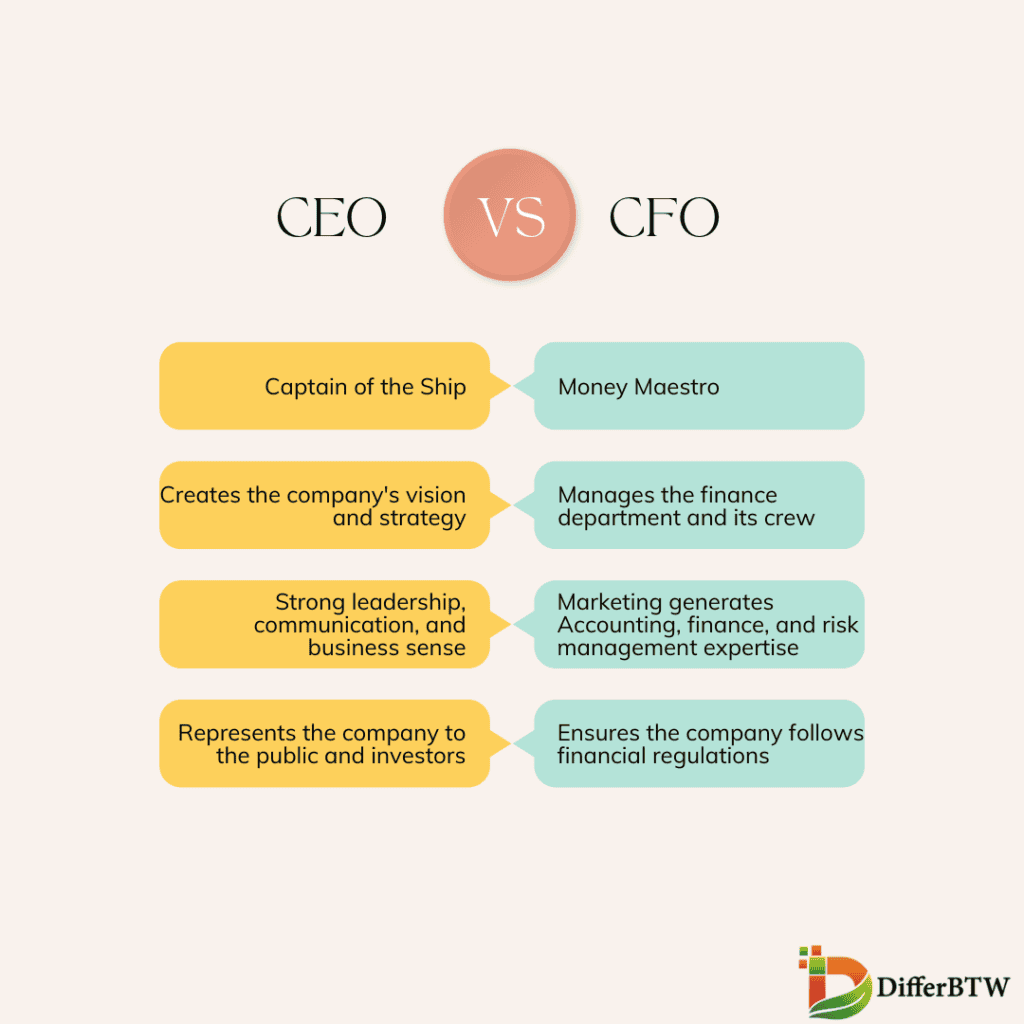
The CEO, or Chief Executive Officer, is the top dog in the company, responsible for setting the overall vision, strategy, and direction of the organization. They’re the ones making the big-picture decisions and leading the charge.
CFO, or Chief Financial Officer, is focused on the financial health and stability of the company. They’re the ones crunching the numbers, creating budgets, and ensuring that the company is profitable and financially sound. While the CEO is more outward-facing, dealing with stakeholders, media, and the public, the CFO is more inward-facing, working closely with the accounting and finance teams to keep everything running smoothly.
Comparison Chart
| Parameter of Comparison | CEO (Chief Executive Officer) | CFO (Chief Financial Officer) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Overall company strategy, mission, and direction | Financial health and performance |
| Responsibilities | * Setting strategic goals and objectives * Leading and motivating employees * Overseeing all departments * Building and maintaining relationships with investors and stakeholders * Representing the company to the public * Making major business decisions | * Managing the finance department * Overseeing financial reporting (e.g., budgets, forecasts) * Risk management and financial compliance * Financial analysis and interpreting financial data * Capital allocation and fundraising * Mergers and acquisitions (financial aspects) |
| Skills | * Strong leadership and communication skills * Visionary thinking and strategic planning * Business acumen and industry knowledge * Ability to build and maintain relationships | * Accounting and financial expertise * Analytical and problem-solving skills * Risk management skills * Strong communication and presentation skills * Understanding of financial regulations |
| Background | Can come from various departments (sales, marketing, operations) | Typically comes from an accounting or finance background |
| Reporting To | Board of Directors | CEO |
What is CEO?
A CEO is the prominent executive of a corporation, business or non-profit organization. They are the primary decision-makers and run the management of a company. CEOs are chosen based on their leadership abilities and experience. Most corporations have a chief executive, but not all have one.
A CEO’s role is to manage a company’s internal resources and workforce. CEO oversees the daily operations of the company. CEO direct the business’s strategy and plan business growth. A CEO acts as a spokesperson for the company and explains the company’s operations to the public. CEOs oversee everything that goes on inside a business; they have total control over their business.
CEO ensure that all decisions they make are always ethical. A CEO oversees everything inside a business; they must have strong communication skills to communicate their goals to the public effectively.

The Role of a CEO
The CEO’s primary role is to ensure that the company is running efficiently and effectively, making strategic decisions that will benefit the organization in the long run. Some of the key responsibilities of a CEO include:
Setting the Company’s Strategy
The CEO is responsible for developing and implementing the company’s strategic vision. This involves setting long-term goals, identifying opportunities for growth, and making decisions about how to allocate resources to achieve those goals.
Making Major Corporate Decisions
From mergers and acquisitions to expanding into new markets, the CEO is responsible for making the big decisions that will shape the future of the company. These decisions often involve weighing the potential risks and rewards and considering the impact on all stakeholders, including employees, customers, and shareholders.
Managing the Company’s Operations
The CEO oversees the day-to-day operations of the company, ensuring that everything is running smoothly and efficiently. This involves working closely with other senior executives, such as the Chief Financial Officer (CFO) and Chief Operating Officer (COO), to manage the various departments and functions within the organization.
Representing the Company
As the face of the company, the CEO is often responsible for representing the organization to external stakeholders, such as investors, media, and the general public. This involves communicating the company’s vision, values, and performance to these groups and building relationships with key partners and customers.
The Skills and Qualities of a Successful CEO
To be an effective CEO, one must possess a unique combination of skills and qualities. Some of the most important include:
Strong Leadership Skills
A CEO must be able to inspire and motivate their team, setting a clear direction for the company and ensuring that everyone is working towards the same goals. This requires strong communication skills, the ability to make tough decisions, and the confidence to take calculated risks.
Strategic Thinking
CEOs must be able to think strategically, anticipating future trends and challenges and developing plans to position the company for success. This requires a deep understanding of the industry, as well as the ability to analyze complex data and make informed decisions based on that information.
Adaptability
In today’s fast-paced business environment, CEOs must be able to adapt quickly to changing circumstances. This means being open to new ideas, embracing change, and being willing to pivot when necessary.
Emotional Intelligence
CEOs must be able to build and maintain strong relationships with their team, customers, and other stakeholders. This requires a high level of emotional intelligence, including empathy, self-awareness, and the ability to manage one’s own emotions and those of others.
The Path to Becoming a CEO
There is no one-size-fits-all path to becoming a CEO, but there are several common routes that many successful executives have taken. These include:
Education
Most CEOs have at least a bachelor’s degree, often in a field such as business, finance, or management. Many also have advanced degrees, such as an MBA or a master’s in a specific industry or function.
Experience
CEOs typically have many years of experience in their industry, often starting in entry-level positions and working their way up through the ranks. Along the way, they develop a deep understanding of the business, as well as the leadership and management skills necessary to succeed at the highest levels.
Networking
Building strong relationships with others in the industry is key to becoming a CEO. This involves attending industry events, joining professional organizations, and seeking out mentorship opportunities with experienced executives.
The Challenges of Being a CEO
While being a CEO can be an incredibly rewarding and fulfilling career, it also comes with its share of challenges. Some of the most significant include:
Managing Competing Priorities
CEOs often have to balance the needs and expectations of various stakeholders, including employees, customers, shareholders, and the board of directors. This can involve making difficult trade-offs and decisions that may not please everyone.
Dealing with Uncertainty
In today’s rapidly changing business environment, CEOs must be comfortable with uncertainty and ambiguity. This means being able to make decisions based on incomplete or constantly evolving information, and being willing to take calculated risks when necessary.
Maintaining Work-Life Balance
The demands of being a CEO can be all-consuming, making it difficult to maintain a healthy work-life balance. CEOs must be disciplined about setting boundaries and carving out time for family, friends, and personal pursuits.
Examples of CEOs
- Elon Musk – The charismatic and sometimes controversial CEO of Tesla and SpaceX, known for his ambitious goals and Twitter presence.
- Tim Cook – The calm and collected CEO of Apple, who took over after Steve Jobs and has led the company to new heights.
- Jeff Bezos – The founder and former CEO of Amazon, who transformed the way we shop and built a massive e-commerce empire.
- Mary Barra – The first female CEO of a major automaker, leading General Motors through a period of innovation and change.
- Satya Nadella – The CEO of Microsoft, credited with revitalizing the company and shifting its focus to cloud computing and AI.
What is CFO?
The CFO, or Chief Financial Officer, is an organization’s second highest-ranking corporate officer. They are responsible for the financial well-being of the company and its shareholders. The CFO oversees the financial department and ensures that the company complies with all financial regulations. In addition, the CFO is responsible for preparing the company’s financial statements and overseeing the company’s budget.
he is responsible for monitoring spending on inventory and breaking down each account to determine how much money is available for expenditures. Essentially, the CFO knows how to manage and use money effectively.
CEOs need to let their CFOs know everything they need to know about their companies to run them effectively. For example, he needs to know which expenses are necessary and which can be cut or delayed without affecting the business. He also needs to know precisely how much money his company has so he can make wise budget decisions. Furthermore, CFO needs to be aware of any tax laws regarding business income so his company can pay its fair share of taxes. A CFO is essential in any business; without one, a company cannot effectively manage its finances.

Key Responsibilities of a CFO
Financial Planning and Analysis
One of my primary responsibilities as a CFO is to oversee the company’s financial planning and analysis. I work with my team to develop detailed financial models, forecasts, and budgets that align with the organization’s short-term and long-term goals. By analyzing financial data and market trends, I provide insights and recommendations to the CEO and board of directors to support informed decision-making.
Financial Reporting and Compliance
As the CFO, I am accountable for ensuring the accuracy and integrity of the company’s financial reporting. My team and I prepare financial statements, such as balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements, in compliance with applicable accounting standards and regulations. I also oversee the internal control systems to mitigate financial risks and ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
Treasury and Cash Management
Managing the company’s treasury and cash flow is another critical aspect of my role. I work closely with the treasury team to optimize cash management, monitor working capital, and ensure sufficient liquidity to meet the organization’s financial obligations. I also explore and implement strategies to maximize returns on investments and minimize financing costs.
Risk Management
As the CFO, I play a vital role in identifying, assessing, and mitigating financial risks that may impact the company. I collaborate with other departments to develop and implement risk management strategies, such as insurance coverage, hedging, and diversification. By proactively managing risks, I help safeguard the organization’s assets and ensure its long-term financial stability.
Strategic Leadership and Partnerships
Strategic Planning
In addition to my financial responsibilities, I am a key contributor to the company’s overall strategic planning process. I work closely with the CEO and other executives to develop and execute strategies that drive growth, profitability, and shareholder value. By providing financial insights and analysis, I help shape the organization’s strategic direction and ensure that financial resources are allocated effectively.
Stakeholder Engagement
As the CFO, I actively engage with various stakeholders, including investors, lenders, and analysts. I communicate the company’s financial performance, strategies, and outlook to these stakeholders through financial reports, presentations, and investor relations activities. By maintaining transparent and effective communication, I help build trust and confidence in the organization’s financial management.
Mergers and Acquisitions
When the company pursues growth through mergers and acquisitions, I play a central role in the process. I work with the CEO and other executives to identify potential targets, conduct due diligence, and negotiate deal terms. My financial expertise is crucial in assessing the financial viability and synergies of potential acquisitions and ensuring a smooth integration process.
Examples of CFOs
- Ruth Porat – The CFO of Alphabet (Google’s parent company), known for her financial discipline and role in the company’s success.
- Luca Maestri – Apple’s CFO, working closely with Tim Cook to manage the company’s massive cash reserves and financial operations.
- Amy Hood – Microsoft’s CFO, playing a key role in the company’s transition to cloud computing and its acquisition strategy.
- Catherine Lesjak – The former CFO of HP, who helped navigate the company through a period of major restructuring and split.
- David Wehner – Facebook’s CFO, responsible for managing the company’s finances through periods of rapid growth and controversy.
Differences Between CEO and CFO
Job Focus
- The CEO is the top dog, the big cheese, the one who sets the overall direction and strategy for the entire company. They’re responsible for making sure the company is on the right track and achieving its goals.
- The CFO is like the financial wizard behind the scenes. They focus on managing the company’s financial health, making sure there’s enough cash flow, and that the books are balanced.
Decision-Making
- The CEO is the ultimate decision-maker. They have the final say on major company decisions, like expanding into new markets, launching new products, or making big investments.
- The CFO provides valuable input and advice on financial matters to help the CEO make informed decisions. They crunch the numbers and give the CEO the lowdown on the financial implications of different options.
Reporting Structure
- The CEO is at the top of the food chain and reports directly to the board of directors. They’re accountable to the board and shareholders for the company’s overall performance.
- The CFO usually reports to the CEO. They keep the CEO in the loop about the company’s financial situation and make sure the CEO has the financial info they need to steer the ship.
External Responsibilities
- The CEO is often the face of the company. They’re the ones schmoozing with investors, doing media interviews, and representing the company at industry events.
- The CFO is more behind the scenes but still has important external responsibilities. They work closely with investors, lenders, and auditors to make sure the company’s finances are shipshape.
Strategic Planning
- The CEO is the mastermind behind the company’s long-term strategy. They look at the big picture and decide where the company should be heading in the next 5, 10, or even 20 years.
- The CFO is like the reality check for the CEO’s grand plans. They make sure the company has the financial resources to make those plans a reality and help develop financial strategies to support the company’s goals.
Risk Management
- The CEO is responsible for overall risk management. They identify potential risks to the company and develop strategies to mitigate them.
- The CFO focuses on financial risk management. They keep an eye on things like credit risk, liquidity risk, and market risk, and put measures in place to protect the company’s financial assets.
People Management
- The CEO is the leader of the pack. They’re responsible for hiring and managing the company’s top executives, and setting the overall company culture.
- The CFO manages the finance team and works closely with other department heads to make sure everyone’s on the same page when it comes to the company’s finances.