The Bank Rate and the Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) Rate are like two siblings in the vast financial landscape, each with its unique role in the central banking family. Think of the Bank Rate as the older, wiser sibling, setting the tone for interest rates in the economy.
It’s the benchmark rate at which the central bank lends to commercial banks for the long haul. Now, meet the MSF Rate, the younger, edgier sibling, designed for those urgent late-night financial emergencies.
This rate allows banks to tap into immediate funds when they’ve exhausted other avenues, but it comes at a slightly higher cost. Together, these rates orchestrate a monetary symphony, balancing the need for stability with the flexibility to navigate unforeseen financial crescendos.
Comparison Chart
| Feature | Bank Rate | MSF Rate |
|---|---|---|
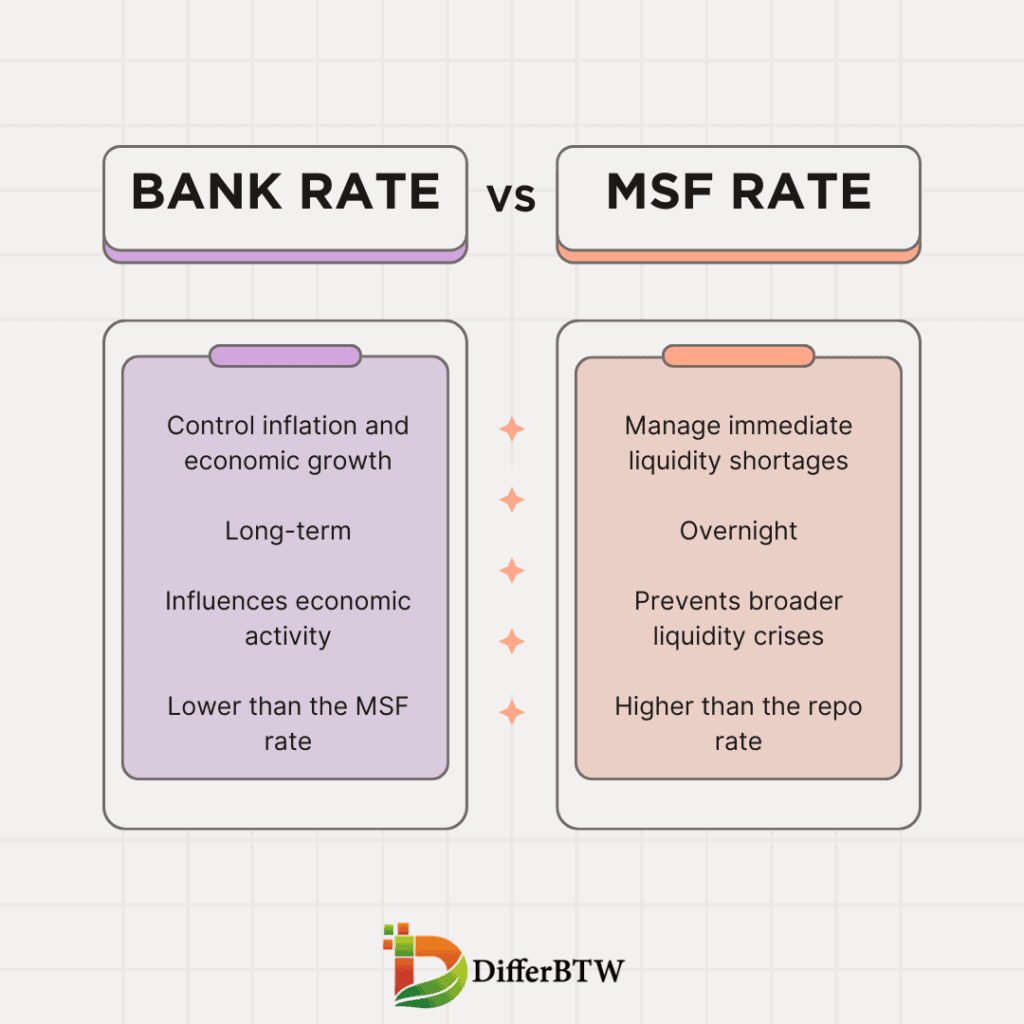
| Meaning | The rate at which the central bank lends long-term funds to commercial banks. | The rate at which the central bank lends short-term funds to commercial banks as a last resort. |
| Purpose | To control inflation and economic growth (long-term policy tool). | To manage immediate liquidity shortages in the banking system (short-term tool). |
| Frequency of Change | Changed infrequently, a few times a year based on economic conditions. | Can be changed more frequently, even daily, depending on liquidity needs. |
| Term of Borrowing | Long-term (for a year or more). | Overnight (one day only). |
| Availability | Not readily available; banks need to present a specific justification for borrowing. | Available to all scheduled commercial banks as a last resort, subject to limits. |
| Interest Rate | Typically lower than the MSF rate, as it’s not considered a penalty rate. | Typically higher than the repo rate and the bank rate, acting as a disincentive for overuse. |
| Impact on Borrowers | Affects interest rates on long-term loans offered by commercial banks (e.g., mortgages, business loans). | Has minimal direct impact on borrowers, but indirectly affects interest rates on short-term loans if banks become reliant on MSF. |
| Impact on Economy | A significant tool for influencing economic activity and inflation. | Helps maintain financial stability and prevent broader liquidity crises. |
Similarities Between Bank Rate and MSF Rate
1. Lender of Last Resort Function
Both the Bank Rate and MSF Rate serve as tools for the central bank to act as the lender of last resort. They provide a mechanism for banks to access funds in times of need, ensuring the stability of the financial system.
2. Influence on Interest Rates
Both rates play a crucial role in influencing overall interest rates in the economy. Changes in these rates have a cascading effect on the interest rates offered by commercial banks, affecting borrowing and lending activities.
3. Monetary Policy Implementation
Bank Rate and MSF Rate are integral components of a central bank’s monetary policy toolkit. They are adjusted strategically to achieve the broader macroeconomic objectives, such as controlling inflation, promoting economic growth, and maintaining financial stability.
What is Bank Rate?
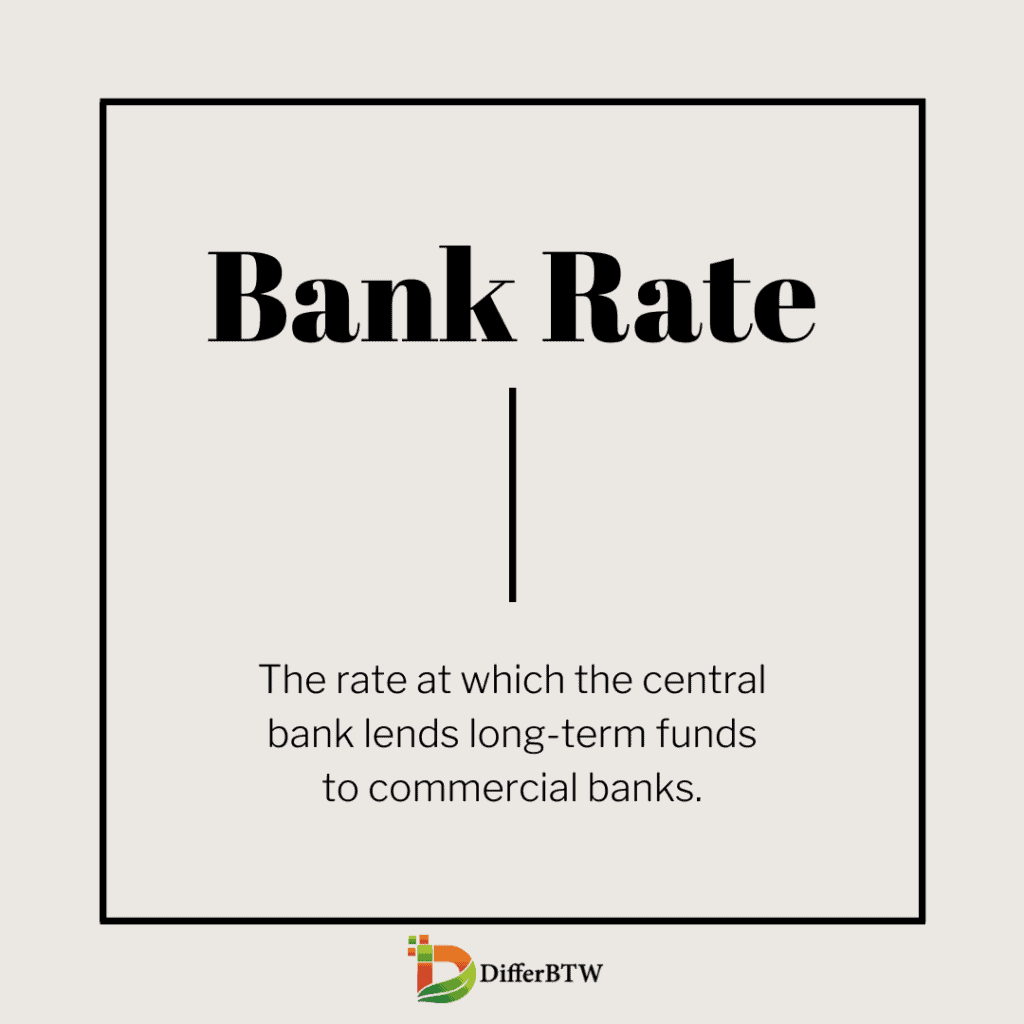
The bank rate refers to the interest rate at which a central bank lends money to commercial banks within a country. Also known as the discount rate, it plays a crucial role in monetary policy. Central banks use the bank rate as a tool to influence the overall money supply in the economy, control inflation, and regulate economic growth.
Determinants of Bank Rate
Several factors influence the setting of the bank rate:
1. Economic Conditions
The prevailing economic conditions, such as inflation rates, unemployment levels, and overall economic growth, play a significant role in determining the appropriate bank rate. Central banks adjust the rate to align with their monetary policy objectives.
2. Inflation Targeting
Central banks set inflation targets as part of their monetary policy framework. The bank rate is adjusted to ensure that inflation remains within the target range. If inflation is rising, a higher bank rate may be implemented to cool economic activity.
3. Exchange Rates
The bank rate also has an impact on exchange rates. A higher bank rate can attract foreign capital seeking better returns, leading to an appreciation of the domestic currency. Conversely, a lower rate may contribute to currency depreciation.
Functions of Bank Rate
1. Controlling Inflation
One of the primary functions of the bank rate is to control inflation. By adjusting the interest rate, central banks influence the borrowing costs for banks, affecting their lending practices and, consequently, the spending patterns of businesses and consumers.
2. Managing Economic Growth
Central banks utilize the bank rate to manage economic growth. During periods of rapid expansion, a higher rate can be employed to curb excessive borrowing and spending, while a lower rate is used to stimulate economic activity during downturns.
3. Liquidity Management
The bank rate also serves as a tool for managing liquidity in the financial system. By adjusting the cost of borrowing, central banks can influence the amount of money in circulation, ensuring stability in the financial markets.
Impact on Financial Markets
Changes in the bank rate have a profound effect on financial markets:
1. Interest Rates
The bank rate directly influences the interest rates offered by commercial banks. An increase in the bank rate leads to higher lending rates, affecting borrowing costs for businesses and consumers.
2. Bond Prices
Bond prices move inversely to interest rates. When the bank rate rises, bond prices tend to fall, impacting the value of fixed-income securities in the market.
3. Stock Markets
Fluctuations in the bank rate can influence stock markets. Higher rates may lead to lower stock prices as borrowing becomes more expensive for companies, affecting their profitability.
What is MSF Rate?
The Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) Rate is a monetary policy tool employed by central banks, including the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). It serves as a crucial element in the framework designed to regulate short-term liquidity in the financial system. Understanding the MSF Rate involves delving into its purpose, calculation, and implications for the economy.

Purpose of MSF Rate
The primary purpose of the MSF Rate is to provide a window for banks to meet their immediate liquidity needs, particularly during unforeseen or exceptional circumstances. It acts as a safety valve, allowing banks to borrow funds overnight from the central bank when they face a temporary shortage of funds. The utilization of the MSF Rate helps maintain stability in the financial markets by preventing abrupt disruptions due to liquidity constraints.
Calculation of MSF Rate
The MSF Rate is set at a fixed percentage above the repo rate, another key policy rate. The repo rate is the rate at which banks borrow money from the central bank by selling their securities with an agreement to repurchase them at a later date. The MSF Rate, being higher than the repo rate, serves as a penal rate, discouraging banks from overly relying on this facility for their funding needs. The specific percentage above the repo rate can vary and is determined by the central bank based on prevailing economic conditions.
Operational Mechanics
Banks can access the MSF by pledging approved government securities as collateral. The central bank, in return, provides funds to the banks at the MSF Rate. This facility is used for short-term liquidity requirements and is subject to certain limits imposed by the central bank to ensure responsible and controlled usage.
Implications for Monetary Policy
Changes in the MSF Rate can signal the stance of monetary policy. An increase in the MSF Rate may indicate a tightening of monetary policy, as it becomes more expensive for banks to borrow funds from the central bank. Conversely, a decrease in the MSF Rate may suggest a more accommodative monetary policy stance, providing banks with relatively cheaper access to funds.
Difference Between Bank Rate and MSF Rate
- Definition:
- Bank Rate: It is the interest rate at which a country’s central bank lends money to commercial banks. It serves as a benchmark for interest rates in the economy.
- Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) Rate: This is the rate at which scheduled commercial banks can borrow funds overnight from the central bank against government securities.
- Purpose:
- Bank Rate: Primarily used to influence the general level of interest rates in the economy, control credit expansion, and achieve monetary policy objectives.
- MSF Rate: Provides a facility for banks to meet their liquidity needs when there is a sudden shortfall, ensuring stability in the financial system.
- Applicability:
- Bank Rate: Applicable for longer-term loans and instruments, influencing the overall interest rate environment.
- MSF Rate: Applicable for short-term liquidity needs, used in emergency situations.
- Interest Rate Differential:
- Bank Rate: Generally lower than the MSF rate, reflecting its role as a long-term policy rate.
- MSF Rate: Higher than the Bank Rate, reflecting the immediate and short-term nature of funds borrowed through this facility.
- Collateral Requirement:
- Bank Rate: Typically involves traditional collateral requirements for loans.
- MSF Rate: Banks can use government securities as collateral, making it more accessible in times of urgent need.
- Access by Banks:
- Bank Rate: Accessible to banks under normal circumstances, and the borrowing process is planned.
- MSF Rate: Intended for rare and unforeseen situations, providing a quick source of funds to maintain liquidity.
- Role in Monetary Policy:
- Bank Rate: Essential tool for monetary policy, influencing economic activity and inflation over the medium to long term.
- MSF Rate: Addresses short-term liquidity issues and ensures financial stability without compromising long-term policy objectives.
- Frequency of Utilization:
- Bank Rate: Regularly utilized by banks for planned borrowing to meet their capital requirements.
- MSF Rate: Infrequently used, during sudden liquidity crises or emergencies.